Sewa Cloud Server Pertimbangan Sebelum Memilih
Sewa Cloud Server: Pertimbangan Sebelum Memilih is a crucial decision for businesses in Indonesia, impacting operational efficiency, cost, and security. Understanding your specific needs, from workload demands to scalability requirements, is paramount. This guide navigates the complexities of choosing a cloud server, helping you evaluate providers, configurations, and cost implications to make an informed decision that aligns perfectly with your business goals.
Choosing the right cloud server provider and configuration can be a daunting task. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the intricacies of cloud server selection in Indonesia. We’ll explore various factors, from understanding your specific business needs and comparing leading providers to optimizing performance and managing costs effectively. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to choosing a cloud server solution that perfectly suits your requirements.
Understanding Your Needs
Choosing the right cloud server requires a thorough understanding of your specific needs. This involves analyzing your workload, identifying the appropriate service model, and determining the necessary server specifications. Failing to do so can lead to underperforming infrastructure or unnecessary expenses.
Typical Workloads in Indonesia, Sewa Cloud Server: Pertimbangan Sebelum Memilih
The typical workload for a cloud server in Indonesia is diverse, reflecting the country’s growing digital economy. Common uses include hosting websites and web applications (e-commerce, social media, blogs), running databases for various businesses, supporting software development and testing environments, and enabling remote access to resources for businesses and individuals. The increasing popularity of mobile applications also contributes significantly to the demand for cloud servers, particularly those with high bandwidth and scalability capabilities. Furthermore, many Indonesian businesses are increasingly adopting cloud solutions for disaster recovery and business continuity, further diversifying the workload demands.
Cloud Server Service Models
Several cloud server service models cater to different needs and technical expertise levels. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides the most control, offering virtual machines (VMs) with customizable specifications (CPU, RAM, storage, operating system). Users manage the operating system and applications. Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a more abstracted environment, focusing on application deployment and management. The cloud provider handles the underlying infrastructure, operating system, and middleware. Choosing between IaaS and PaaS depends on the level of control and management desired. Businesses with in-house expertise often prefer IaaS, while those prioritizing faster deployment and simpler management may opt for PaaS.
Determining Server Specifications
Choosing the correct server specifications – CPU, RAM, and storage – is crucial for optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. The required CPU power depends on the computational demands of your applications. High-traffic websites or applications requiring complex processing need more powerful CPUs. RAM determines how much data the server can hold in active memory, impacting application responsiveness. Applications requiring large datasets or numerous simultaneous users need more RAM. Storage capacity depends on the size of your data and applications. Consider using solid-state drives (SSDs) for faster performance compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). For example, a small e-commerce site might need a modest configuration, while a large-scale online game would require significantly more resources.
Cloud Server Pricing Models
Different cloud providers offer various pricing models. Understanding these models is essential for budget planning.
| Pricing Model | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pay-as-you-go | Pay only for the resources consumed. | Cost-effective for fluctuating workloads. | Can be difficult to budget for long-term projects. |
| Reserved Instances | Pre-purchase resources at a discounted rate for a fixed period. | Cost savings for consistent workloads. | Requires commitment and may lead to wasted resources if demand decreases. |
| Spot Instances | Access unused computing capacity at significantly reduced prices. | Highly cost-effective for non-critical workloads. | Instances can be terminated with short notice. |
| Dedicated Hosts | Entire physical server dedicated to a single customer. | Enhanced security and isolation. | Higher cost compared to shared resources. |
Evaluating Cloud Server Providers
Choosing the right cloud server provider is crucial for the success of your online projects. A thorough evaluation process ensures you select a provider that aligns with your specific needs and budget, offering the reliability, security, and support necessary for optimal performance. This section will guide you through the key considerations when comparing Indonesian cloud server providers.
Comparison of Indonesian Cloud Server Providers
Several major Indonesian cloud server providers offer a range of services. Direct comparison is difficult without specific service requirements, but a general overview of three prominent providers – (Note: Replace these with actual Indonesian providers and their services; I cannot provide specific company names without potentially inaccurate information) Provider A, Provider B, and Provider C – can highlight key differences. Provider A might be known for its strong focus on enterprise-level solutions and robust security features, while Provider B may emphasize affordability and ease of use, catering more to smaller businesses and individual developers. Provider C could specialize in specific niches like high-performance computing or big data analytics. A detailed comparison would require examining pricing models, service level agreements (SLAs), and the specific features offered within each provider’s service catalog. Consider the geographic location of their data centers and their network infrastructure to assess latency and connectivity for your target audience.
Criteria for Evaluating Reliability and Uptime
Reliability and uptime are paramount for any cloud server. Key criteria for evaluating a provider’s performance in these areas include their Service Level Agreements (SLAs), which should clearly define guaranteed uptime percentages and compensation for outages. Investigate the provider’s infrastructure redundancy – do they utilize multiple data centers, geographically diverse, with failover mechanisms to ensure minimal disruption in case of hardware failure or natural disasters? Examine their network architecture and its capacity to handle peak loads. Look for independent third-party reviews and reports that verify their claims of reliability and uptime. A provider with a proven track record and consistent high uptime is crucial for minimizing business interruptions.
Importance of Security Features
Security is a critical aspect of choosing a cloud server provider. Providers should offer a robust suite of security features, including data encryption both in transit and at rest, access control mechanisms like multi-factor authentication (MFA), regular security audits and penetration testing, and compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations (e.g., ISO 27001). Investigate their security incident response plans – how quickly do they respond to security breaches and what measures do they take to mitigate the impact? Transparency in security practices and regular communication regarding security updates are also vital indicators of a provider’s commitment to security. The provider’s physical security measures for their data centers should also be considered.
Support Options and Responsiveness
Effective support is essential for troubleshooting issues and ensuring smooth operation. Evaluate the different support channels offered by each provider – phone, email, chat, and ticketing systems. Investigate their support hours and response times. Look for documentation and knowledge bases that offer self-service options for resolving common problems. Consider the level of technical expertise offered by their support staff. Read reviews and testimonials to gauge the responsiveness and helpfulness of their support teams. A provider with readily available, knowledgeable, and responsive support is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring efficient problem resolution.
Choosing the Right Server Configuration
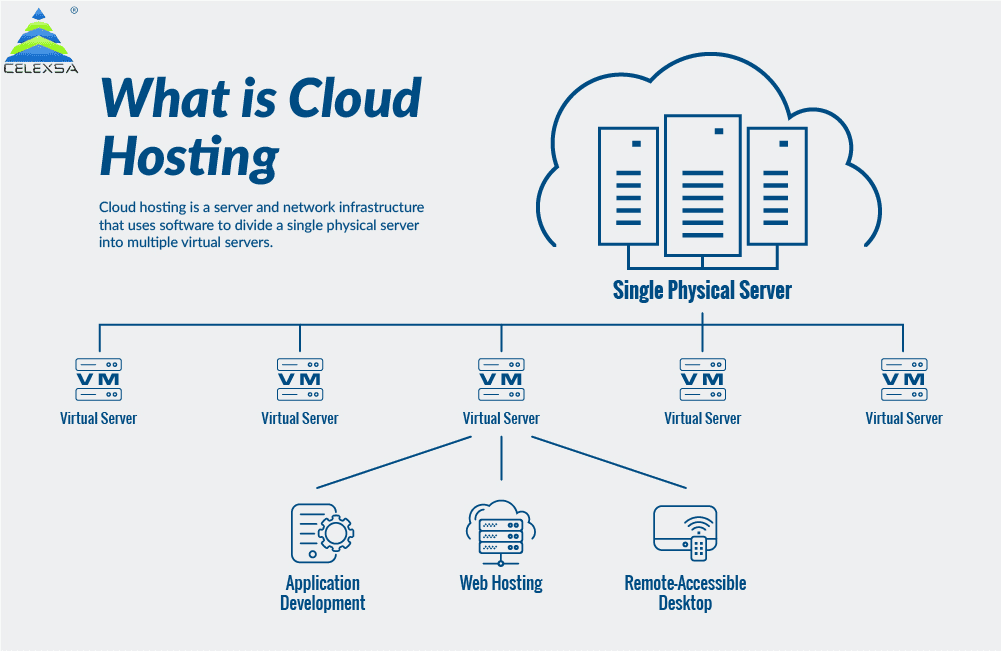
Selecting the appropriate cloud server configuration is crucial for the success of your online presence. A well-configured server ensures optimal performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. This section will guide you through the process of choosing the right specifications for your needs, focusing on considerations relevant to small businesses in Indonesia.
Sample Cloud Server Configuration for a Small Business Website in Indonesia
For a small business website in Indonesia with moderate traffic (e.g., a few hundred visitors per day), a cost-effective and reliable configuration could include:
- Virtual Machine (VM): A virtual machine offers flexibility and cost-efficiency for smaller businesses. The specific type of VM would depend on the chosen cloud provider (e.g., a standard or general-purpose VM).
- CPU: 2 vCPUs (virtual CPUs) should suffice for initial needs. This can be scaled up later if necessary.
- RAM: 4 GB of RAM is generally adequate for a small website. This allows for smooth operation and efficient handling of website traffic.
- Storage: 50 GB of SSD storage should be sufficient for a website with moderate content and data. SSD storage offers faster read/write speeds compared to traditional HDD storage, resulting in improved website performance.
- Operating System: A Linux distribution like Ubuntu or CentOS is recommended for its cost-effectiveness, security features, and wide community support.
- Bandwidth: A bandwidth allocation of 1 TB per month should be more than enough for a small business website. This can be adjusted based on actual usage.
This configuration provides a solid foundation for a small business website, offering a balance between performance and cost. It can be easily scaled up or down as the business grows or traffic demands change.
Virtual Machines (VMs) versus Dedicated Servers
The choice between virtual machines (VMs) and dedicated servers involves trade-offs between cost, performance, and control.
- Virtual Machines (VMs): VMs share the resources of a physical server with other VMs. This results in lower costs and greater flexibility, as resources can be easily scaled up or down as needed. However, performance can be impacted if the physical server is overloaded.
- Dedicated Servers: Dedicated servers provide exclusive access to the entire physical server’s resources. This offers superior performance and greater control over the server environment. However, dedicated servers are significantly more expensive than VMs and require more technical expertise to manage.
For a small business website in Indonesia, a VM is generally a more cost-effective and practical choice, offering sufficient performance for moderate traffic levels. Dedicated servers become more attractive as traffic and resource demands increase significantly.
Operating System and Software Selection
The choice of operating system (OS) and software is crucial for security, performance, and compatibility.
- Operating System: Linux distributions (like Ubuntu or CentOS) are popular choices for their security, stability, and cost-effectiveness. Windows Server is another option, but it typically comes with higher licensing costs. The choice often depends on the software and applications the website requires.
- Software: The website’s content management system (CMS), database system, and other applications must be compatible with the chosen OS. Popular CMS options include WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal. Database systems like MySQL or PostgreSQL are common choices for web applications.
Careful consideration of OS and software compatibility is essential to ensure smooth operation and avoid potential conflicts. Choosing widely-supported options often reduces the risk of encountering compatibility issues.
Optimizing Server Performance and Resource Utilization
Optimizing server performance and resource utilization is crucial for maintaining a responsive and efficient website. Several best practices can help achieve this.
- Regular Software Updates: Regularly updating the OS, CMS, and other software components is crucial for security and performance. Updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements.
- Caching Mechanisms: Implementing caching mechanisms (e.g., server-side caching, CDN) can significantly reduce server load and improve website speed. Caching stores frequently accessed data in memory, reducing the need to access the database or other resources repeatedly.
- Database Optimization: Optimizing database queries and indexing can improve database performance, reducing the time it takes to retrieve data. Regular database maintenance is also important.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Using a CDN distributes website content across multiple servers globally, reducing latency for users in different locations. This is particularly beneficial for websites with a geographically dispersed audience.
- Monitoring and Logging: Regularly monitoring server performance and analyzing logs helps identify bottlenecks and potential issues. This proactive approach enables timely intervention and prevents performance degradation.
By implementing these best practices, small businesses can ensure their cloud servers perform optimally, delivering a positive user experience and maximizing resource utilization.
Cost and Scalability Considerations
Choosing a cloud server involves careful consideration of both cost and scalability. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing your budget and ensuring your infrastructure can handle fluctuating workloads and future growth. Failing to plan for these aspects can lead to unexpected expenses and performance bottlenecks.
Cost Estimation Model for Cloud Server Deployment
A comprehensive cost estimation requires analyzing various factors. Consider the following example for a hypothetical one-year deployment:
| Expense Category | Monthly Cost (USD) | Annual Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Compute (virtual machine instances) | 100 | 1200 |
| Storage (cloud storage) | 50 | 600 |
| Networking (bandwidth, data transfer) | 20 | 240 |
| Database (managed database service) | 30 | 360 |
| Managed Services (optional, e.g., monitoring, backups) | 40 | 480 |
| Total Estimated Monthly Cost | 240 | 2880 |
This is a simplified example; actual costs will vary significantly based on the chosen server specifications (CPU, RAM, storage type), operating system, location, and usage patterns. Higher resource consumption will directly increase costs. Additionally, unexpected spikes in usage can lead to significant overruns.
Strategies for Scaling Cloud Server Infrastructure
Cloud servers offer excellent scalability. Strategies for handling fluctuating demands include:
- Vertical Scaling: Increasing the resources (CPU, RAM, storage) of existing virtual machines. This is simpler but has limitations; you eventually reach a maximum resource limit for a single instance.
- Horizontal Scaling: Adding more virtual machines to distribute the workload. This provides greater flexibility and scalability, allowing for handling significantly larger traffic volumes. Auto-scaling features offered by many cloud providers automate this process, adding or removing instances based on predefined metrics (CPU utilization, request rate).
Cloud Server Billing Models
Cloud providers typically offer several billing models:
- Pay-as-you-go: You pay only for the resources consumed, offering flexibility and cost-effectiveness for unpredictable workloads. However, costs can fluctuate significantly.
- Reserved Instances: You commit to using a certain amount of resources for a specified period (e.g., 1 or 3 years). This typically offers significant discounts compared to pay-as-you-go, but lacks flexibility if your needs change.
- Spot Instances: You bid on unused computing capacity, potentially obtaining significant cost savings but with the risk of instances being terminated with short notice.
Managing Cloud Server Costs Effectively
Effective cost management involves several practices:
- Right-sizing Instances: Choose instance sizes appropriate for your workload. Avoid over-provisioning resources unnecessarily.
- Leveraging Reserved Instances: If your workload is relatively stable, consider reserved instances to reduce costs.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Regularly monitor resource utilization and identify areas for optimization. Tools provided by cloud providers assist in this process.
- Utilizing Cost Management Tools: Cloud providers offer tools to track and analyze cloud spending, enabling proactive cost management.
- Auto-Scaling: Implement auto-scaling to automatically adjust resources based on demand, preventing overspending during low-traffic periods and ensuring sufficient capacity during peaks.
Data Security and Disaster Recovery: Sewa Cloud Server: Pertimbangan Sebelum Memilih
Choosing a cloud server involves significant considerations regarding data security and disaster recovery. The potential for data breaches and service disruptions necessitates a proactive approach to safeguard your valuable information and ensure business continuity. This section details common threats, mitigation strategies, compliance requirements, and a checklist for robust security implementation.
Common Security Threats and Mitigation Strategies
Cloud servers, while offering many advantages, are susceptible to various security threats. These include unauthorized access, data breaches, malware infections, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and misconfigurations. Effective mitigation strategies are crucial to minimize these risks. For example, unauthorized access can be mitigated through strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regular security audits. Data breaches can be prevented by employing encryption both in transit and at rest, implementing robust access control mechanisms, and regularly patching vulnerabilities. Malware infections can be minimized through the use of antivirus software, regular system updates, and careful monitoring of network traffic. DoS attacks can be mitigated by using cloud-based DDoS protection services and implementing robust network security measures. Finally, misconfigurations, a common source of vulnerabilities, can be reduced through rigorous configuration management and automated security checks.
Importance of Data Backups and Disaster Recovery Planning
Data loss can have severe consequences for businesses. Therefore, implementing a comprehensive data backup and disaster recovery plan is paramount. Regular backups to geographically separate locations ensure data availability even in the event of a server failure, natural disaster, or cyberattack. A well-defined disaster recovery plan Artikels procedures for restoring data and services, minimizing downtime and business disruption. This plan should include detailed steps for data restoration, system recovery, and communication protocols. Consider using cloud-based backup services that offer features like versioning and automated backups for enhanced data protection. A robust disaster recovery plan is not just about restoring data, but also about maintaining business continuity. For example, a company relying on e-commerce might need a plan to quickly restore its online store, minimizing lost sales during an outage.
Ensuring Data Compliance with Indonesian Regulations
Indonesia has several regulations governing data privacy and security, including the Personal Data Protection Law (UU PDP). Compliance is crucial to avoid penalties and maintain customer trust. This involves implementing measures to protect personal data, obtaining informed consent for data processing, and ensuring data security measures meet regulatory requirements. Organizations must also establish procedures for handling data breaches, including reporting requirements to relevant authorities. Compliance with Indonesian regulations requires a thorough understanding of the applicable laws and the implementation of appropriate technical and organizational measures. Regular audits and assessments are essential to verify ongoing compliance.
Security Measures Checklist Before Deploying a Cloud Server
Before deploying a cloud server, a thorough security assessment and implementation of appropriate measures are crucial. The following checklist Artikels key steps:
- Implement strong password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Enable encryption for data in transit and at rest (e.g., using HTTPS and disk encryption).
- Configure firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems.
- Regularly update operating systems and software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Implement access control lists (ACLs) to restrict access to resources.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing.
- Establish a robust data backup and disaster recovery plan.
- Ensure compliance with relevant Indonesian data protection regulations.
- Implement monitoring and logging to detect and respond to security incidents.
- Establish incident response procedures.
Monitoring and Management

Effective monitoring and management are crucial for ensuring the optimal performance, security, and availability of your cloud server. Proactive monitoring allows you to identify and address potential issues before they impact your applications and services, while diligent management ensures your server remains configured for peak efficiency and security. This section will explore key aspects of monitoring and managing your cloud server environment.
Monitoring your cloud server involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) to gain insights into its health and resource utilization. This data provides a clear picture of your server’s performance, enabling you to identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and proactively address potential issues. Utilizing monitoring tools and dashboards streamlines this process, providing a centralized view of your server’s status and performance metrics.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Their Monitoring
Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for understanding the health and performance of your cloud server. These metrics provide valuable insights into resource utilization, application performance, and overall system stability. Examples of critical KPIs include CPU utilization, memory usage, disk I/O, network traffic, and application response times. By regularly monitoring these KPIs, you can identify potential bottlenecks and proactively address performance issues. For example, consistently high CPU utilization might indicate the need for server upgrades or application optimization, while slow disk I/O could signal the need for faster storage solutions. Regularly analyzing these metrics helps to maintain optimal performance and prevent unexpected outages.
The Importance of Monitoring Tools and Dashboards
Utilizing monitoring tools and dashboards significantly simplifies the process of tracking and analyzing key performance indicators. These tools provide a centralized view of your server’s health and performance, allowing for quick identification of potential problems. Dashboards typically present data in a user-friendly visual format, such as graphs and charts, making it easier to identify trends and anomalies. Many cloud providers offer built-in monitoring tools, while third-party solutions provide more advanced features and integrations. The choice of tool depends on your specific needs and budget, but the benefits of using a dedicated monitoring system far outweigh the cost in terms of improved efficiency and reduced downtime. A well-designed dashboard can display real-time data on CPU usage, memory consumption, network traffic, and disk space, enabling immediate responses to performance fluctuations.
Best Practices for Managing and Maintaining a Cloud Server Environment
Maintaining a healthy and secure cloud server environment requires a proactive approach. Regular updates and patching are crucial to address security vulnerabilities and ensure optimal performance. Implementing robust backup and recovery procedures is essential for protecting your data against unforeseen events such as hardware failures or cyberattacks. Regular security audits should be conducted to identify and address any potential security weaknesses. Additionally, establishing clear roles and responsibilities for server management ensures accountability and efficient problem-solving. Following these best practices helps maintain the stability and security of your cloud server, minimizing disruptions and ensuring business continuity.
Common Cloud Server Management Tasks
Managing a cloud server involves various tasks aimed at ensuring optimal performance, security, and availability. These tasks include: installing and configuring software, managing user accounts and permissions, monitoring resource utilization, applying security patches, backing up data, scaling resources based on demand, and troubleshooting performance issues. For example, regularly updating the operating system and applications helps mitigate security vulnerabilities, while monitoring resource usage helps identify potential bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation. Proactive management minimizes downtime and ensures the continued smooth operation of your applications and services. A well-defined schedule for routine maintenance tasks, such as security patching and software updates, ensures a consistently stable and secure environment.
Outcome Summary
Selecting a cloud server in Indonesia requires careful consideration of various factors, from understanding your unique business needs to evaluating provider reliability and security. By thoroughly assessing your workload demands, comparing providers based on key criteria like uptime, security features, and support, and designing an optimal server configuration, you can ensure a robust and cost-effective cloud solution. Remember that proactive monitoring, robust security measures, and a well-defined disaster recovery plan are essential for long-term success. This informed approach will empower you to make the best decision for your business.
Detailed FAQs
What is the difference between IaaS and PaaS?
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) provides virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networking. PaaS (Platform as a Service) offers a complete platform for application development and deployment, including pre-configured environments and tools.
How do I estimate my cloud server costs?
Cost estimation involves considering factors like server specifications (CPU, RAM, storage), operating system licenses, bandwidth usage, and the chosen billing model (pay-as-you-go, reserved instances). Cloud providers typically offer cost calculators to assist in this process.
What security measures should I prioritize?
Prioritize strong passwords, regular software updates, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, data encryption, and robust access control mechanisms. Consider a multi-factor authentication strategy for enhanced security.
What are the common Indonesian regulations related to cloud data?
Compliance with Indonesian regulations requires understanding laws related to data privacy (like the Personal Data Protection Law) and data sovereignty. It’s advisable to consult legal experts to ensure full compliance.